The Total RNA from Blood Extraction Kit is designed for the isolation of total RNA (longer than 200 bases) from up to 1ml fresh or frozen anti-coagulated whole blood.
Description
The timesaving GF-1 Blood RNA Extraction Kit is designed for rapid and efficient purification of total RNA from up to 1 ml fresh or frozen anti-coagulated whole blood. The purification is based on the usage of 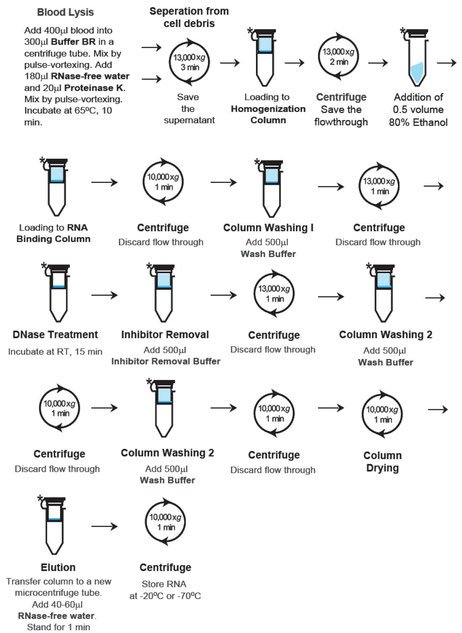 denaturing agents to provide efficient cell lysis, denaturation of proteins and subsequent release of RNA. Special buffers provided in the kit are optimized to enhance the binding of RNA onto a specially-treated glass filter membrane for efficient and fast recovery of highly pure RNA.
denaturing agents to provide efficient cell lysis, denaturation of proteins and subsequent release of RNA. Special buffers provided in the kit are optimized to enhance the binding of RNA onto a specially-treated glass filter membrane for efficient and fast recovery of highly pure RNA.
Features
– Mini-column spin technology.
– Yields up to 4 µg of total RNA.
– No organic-based extraction required.
– Highly pure total RNA, ready to use for RT-PCR, Northern Blotting, polyA RNA (mRNA) purification,
nuclease protection and in vitro translation.
Application
For purification of human total blood RNA.
Kit components:
– Homogenization Columns
– RNA Binding Columns
– Collection tubes
– Buffer BR*
– Inhibitor Removal Buffer*
– Wash Buffer*
– Proteinase K*
– DNase I*
– Digestion Buffer
– Digestion enhancer
– RNase-free Water
– Handbook
* Please refer to Reconstitution of Solutions and Storage and Stability before using this kit.
| Product | Description |
| TB05 | Total RNA from Blood Extraction Kit The Total RNA Extraction Kit is designed for the isolation of total RNA (longer than 200 bases) from up to 1ml fresh or frozen anti-coagulated whole blood. Pack size: 5 preps |
| TB25 | Total RNA from Blood Extraction Kit The Total RNA Extraction Kit is designed for the isolation of total RNA (longer than 200 bases) from up to 1ml fresh or frozen anti-coagulated whole blood. Pack size: 25 preps |
MSDS RNA from Blood Extraction Mini-Prep Kit
Referenzen
Liu, T., Liu, F., Wang, C., Wang, Z., Li,Y. (2017) The boosted biomass and lipid accumulation in Chlorella vulgaris by supplementation of synthetic phytohormone analogs. Bioresource Technology. 232. Pp..44-52
Waziri, P.M., Abdullah, R., Yeap, S.W., Omar, A.R., Abdul, A.B., Kassim, N.K., Malami, I., Karunakaran,T., Imam, M.U. 2016. Clausenidin from Clausena excavata induces apoptosis in hepG2 cells via the mitochondrial pathway. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 194 pp.549-558.
Abu-Elsaad,N.M., Serrya, M.S., El-Karef, A.M., Ibrahim, T.M. (2016).
Kaplan, S. et al. (2016) The Potential of Microarray Databases to Identify Tissue Specific Genes Kafkas Üniversitesi Veteriner Fakültesi Dergisi,22(1), p. 29-35.
Loosse, C., Pawlas, M., Bukhari, H.S.S., Maghnouj, A., Hahn, S., Marcus, K., Müller, T. (2016) )Nuclear spheres modulate the expression of BEST1 and GADD45G. Cellular Signalling. 28. Pp.100-109.
Ng, S.L., Harikkrishna, J.A., Bakar,F.A., Yeo, C.C., Cha, T.S. (2016) Heterologous expression of the Streptococcus pneumoniae yoeB and pezT toxin genes is lethal in Chlorella vulgaris. Algal Research. 19 pp.21-29
Saregah, N., et al (2016) Effects of Phenolic-rich Extracts if Clinacanthus nutans on High Fat and High Cholesterol Diet-induced Insulin Resistance BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine16(88), p.1-11.
Moghadam, F.H., et al. (2015) Differentiation of Rat Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Adipocytes and Cardiomyocytes after Treatment with Platelet Lysate. International Journal of Hematology-Oncology and Stem Cell Research. 10(1), p. 21-29.
Shalabi,M.,Khilo, Kh., Zakaria, M.M., Elsebaei, M.G., Abdo, W., Awadin, W. (2015) Anticancer activity of Aloe vera and Calligonum comosum extracts separetely on hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine. 5(5) pp.375-381.
Hassanin, A., et al. (2014) Heparin Modulation on Hepatic Nitric Oxide Synthase in Experimental Steatohepatitis. Experimental and Theapeutic Medicine. 8, p. 1551-1558.
